The Ultimate Guide to GST Refunds
In India, Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an exasperating activity, especially when it comes to the process of availing refunds. As an exporter or a startup that has surplus ITC or a taxpayer who has an inverted duty structure, it is important to know how the GST refund works to ensure you are not caught short of payment and are also compliant.
What is a GST Refund?
A GST refund refers to the return of excess tax paid by a taxpayer to the government. These may be as a result of various reasons as follows:
- Excess Input Tax Credit (ITC)
- Zero -rated such as exports
- Inverted duty system (we have found that input tax > output tax)
In the CGST Act, the regulation of the refund is by:
Section 54: Deals with the procedure and conditions of claiming GST refunds, such as time limit (usually within a Period of 2 years) and categories such as exports, inverted duty structure, and overpayments.
Section 55: Concerns itself with refunds to the specialised agencies, e.g., the United Nations, the embassies, and the multilateral financial institutions, which can make claims to tax refunds on taxation of the inward supplies.
Section 56: Gives potential issues regarding the interest to be paid by the government in case the refund has not been received within 60 days or has been delayed since receipt of a complete application.
Meaning of GST refund
The provisions provided in section 54 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017, deal with the refund of the tax paid under GST. It establishes different terms and processes of refund claim, the date applicable in determining the time of filing the refund claim, the type of taxes that are refundable, and the documents that should be submitted together with the application for a refund claim.
Who Can Claim a GST Refund?
Under section 54 of the CGST Act, along with Rule 89 of the CGST Act 2017, businesses can claim the GST Refund of accumulated ITC in the following cases:
- In the case where there is an inverted tax structure in the business.
- To the exportation of goods or services produced without the tax (as reported in the Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or bond).
- Whereas there has been a supply to Special Economic Zone (SEZ) units or developers without a payment of taxes.
- By foreign embassies and by international organisations on their intake of goods or services.
- Refund attributed to the end notification of provisional assessments.
- Oversupply in the balance of the electronic cash ledger.
Where there is overpayment of tax as a result of wrong calls or classification.
Cases in which unutilised ITC is not refundable are as below:
- In case the export of goods outside India is subjected to the excise duty, there would be no ITC stored available as a GST refund.
- Where the excise duty paid on the said supply has been claimed as duty drawback by the supplier of goods, or where he has claimed a refund of IGST so paid.
- In the event of an inverted tax structure, the output is nil or GST-free.
GST refund eligibility
Not every taxpayer is eligible; many of them are under the GST regulations. A claim for refund may arise on account of the following situations:
(a) Export of goods or services
(b) Supplies to SEZ units and developers
(c) Supply of goods regarded as Deemed Exports
(d) Refund of taxes on purchases by UN or embassies under Section 55 of the CGST Act, 2017
(f) Refund of the accumulated Input Tax Credit on account of the inverted rate structure
(i) Tax paid in excess/by mistake
(k) Refund of tax paid in the wrong head under Section 77 of the CGST Act, 2017 & Section 19 of the IGST Act, 2017
Thus, practically every situation is covered. The GST law requires that every claim for refund be filed within 2 years from the relevant date
Types of GST Refunds
Your refund category will also change depending on the nature of your business and the kind of transaction that you are making.
These are the various categories of refunds under the GST regime as given below:
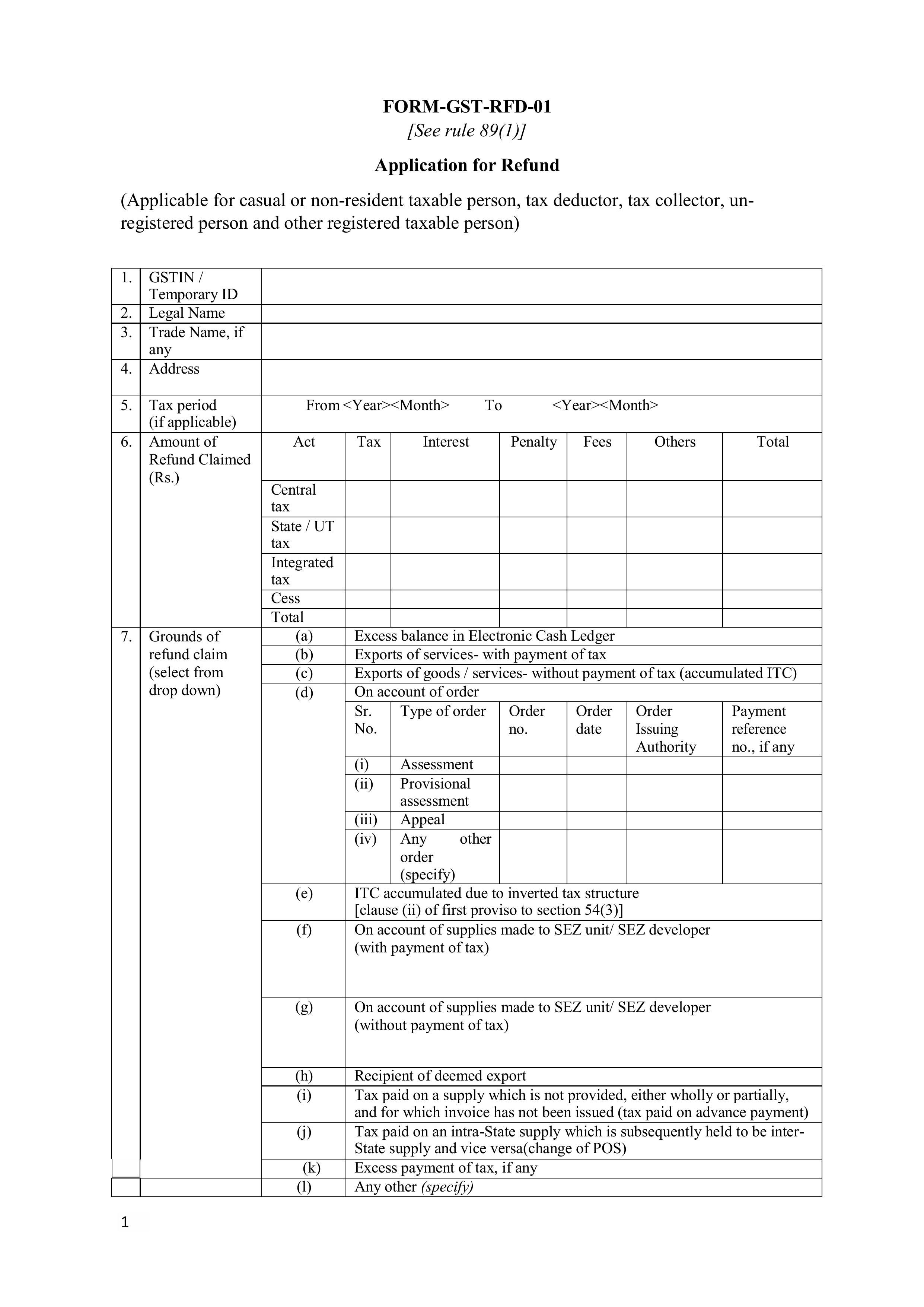

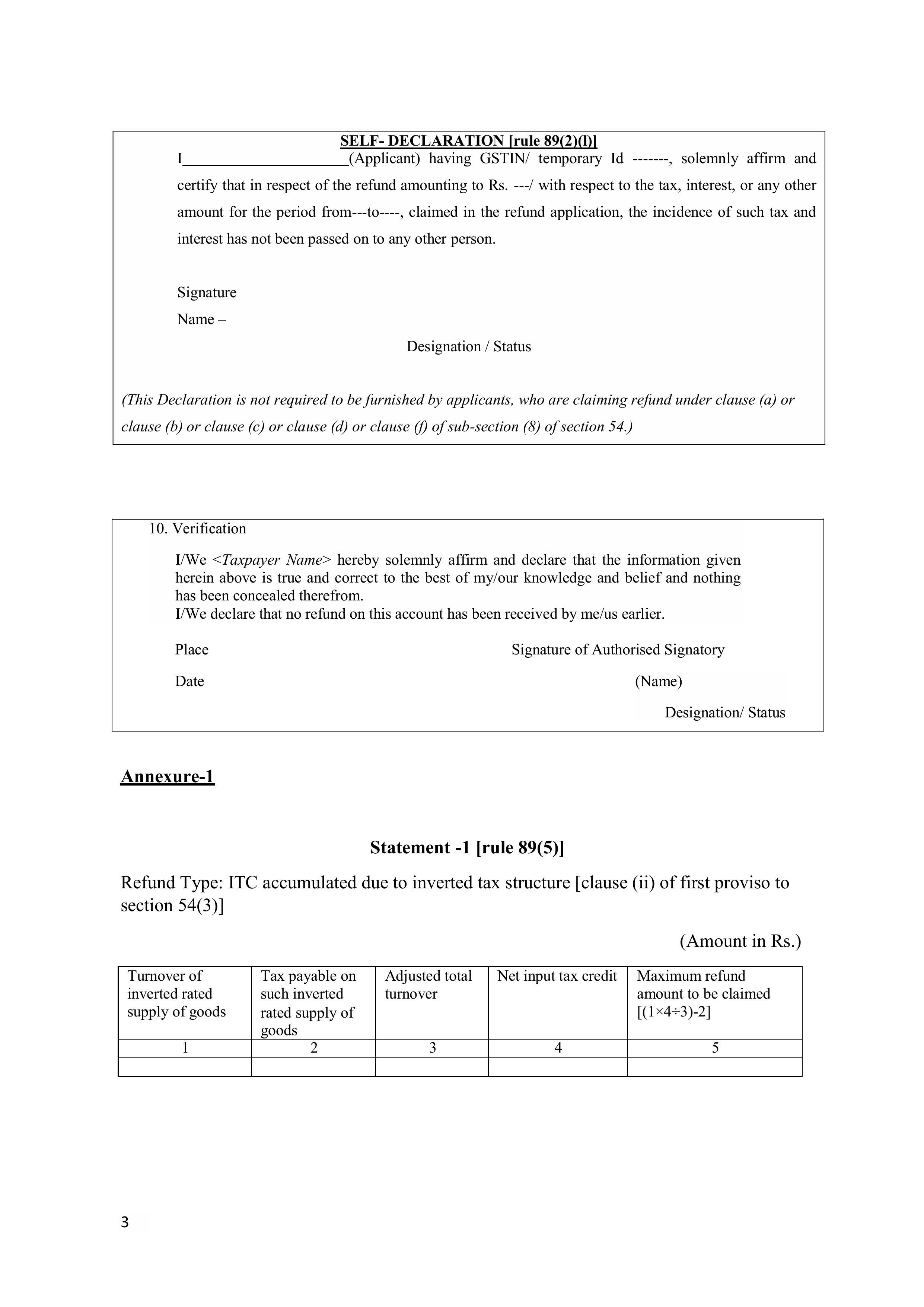
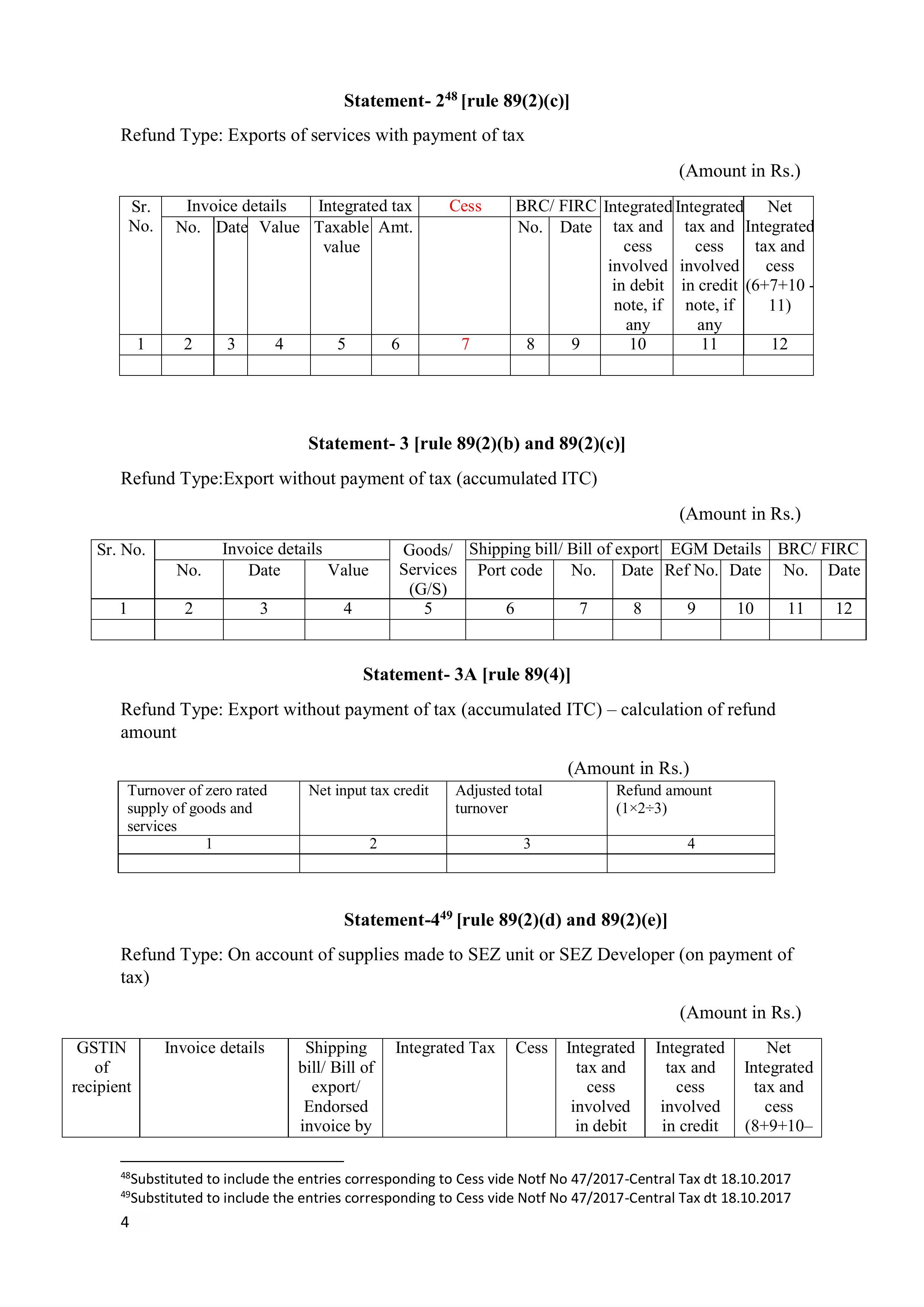
GST refund on Exports
- Reimbursement of GST charged on supplies given to SEZ units.
- Refund of GST paid on the amount of excess tax/provisional assessment.
- Refund of GST on purchases made by UN bodies.
- The ITC that was not used will be refunded due to export.
Refund based on any other ground or reason.
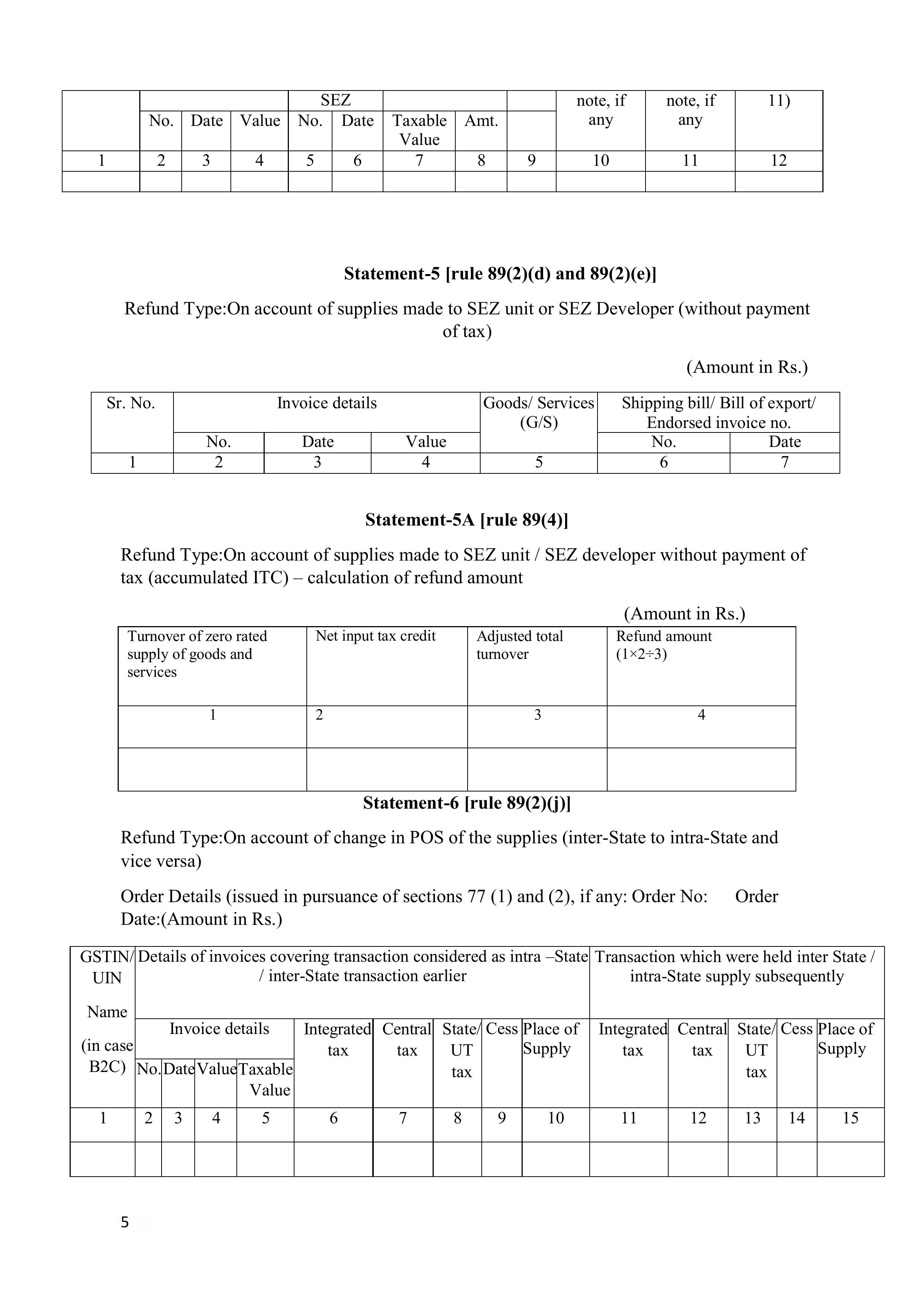
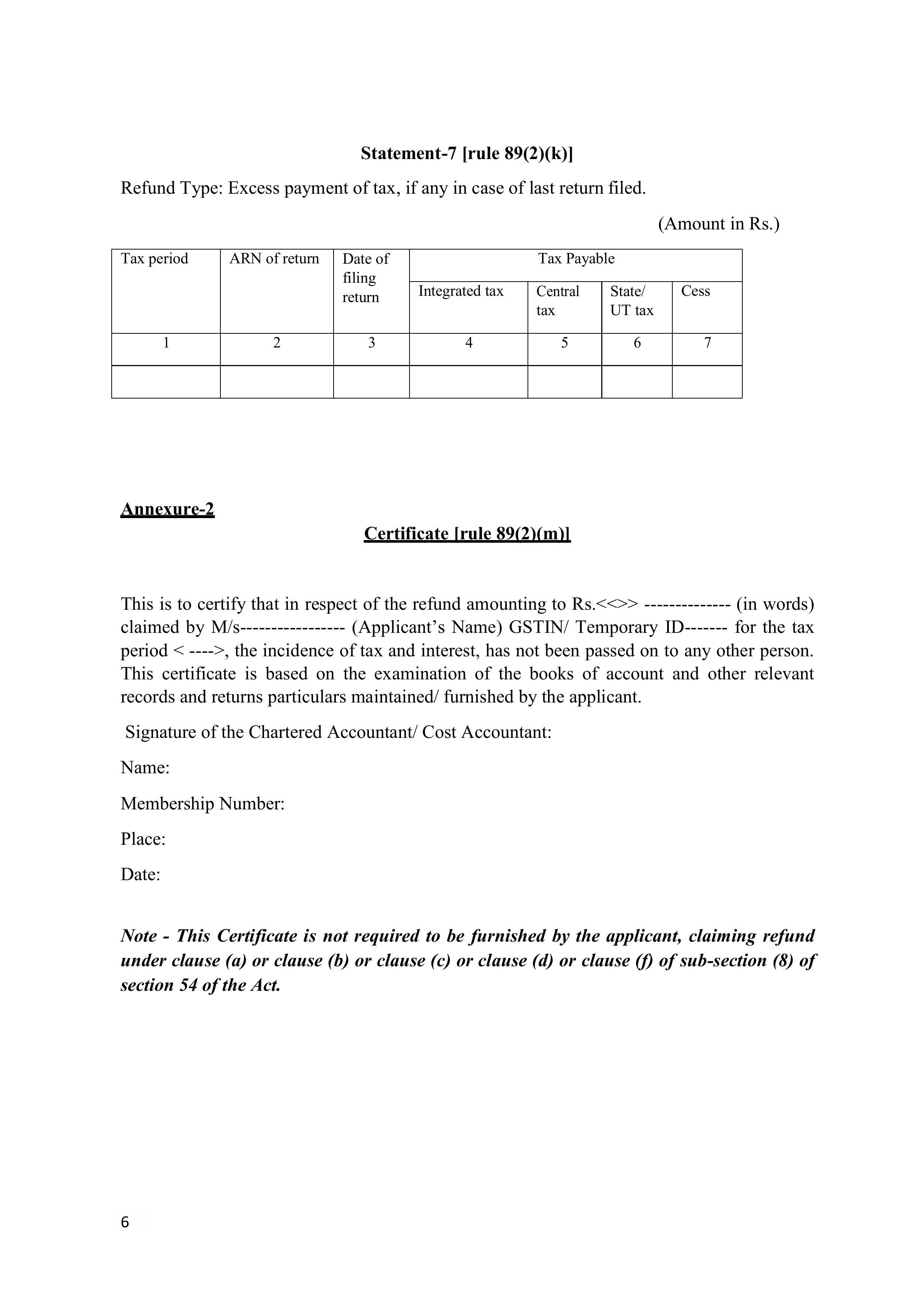


GST refund on inverted dut
Under the existence of Input tax and output tax, the accumulation of Input Tax Credit (ITC) occurs when the tax rate on the input (purchases) is higher than that of taxes on output supplies. This becomes what is called the inverted duty structure. Under Section 54(3) of the CGST Act, a taxpayer is allowed to get a refund of the unused ITC in these instances.
The application for refund should be made by filing the application for refund form, GST RFD-01, following the filing of relevant GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B returns of the tax period. The supporting records, such as statement of invoices, inward and outward supply particulars, declarations as per Rule 89(5), are required. There are also prescribed conditions that should be satisfied by the taxpayer, that are mentioned in Rule 89(2)(h) and Rule 89(5).
Note: ITC refund cannot be made in regard to input services or capital goods during the inverted duty structure.
GST refund time limit
- The application for a refund should be made within the Period of 2 years following the event that is to be refunded (e.g., date of export).
- Failure to process within 60 days results in interest of 6 percent payable to the department.
- The lowest possible value of refund concerning a valid claim is 1,000 rupees.
How to file a GST refund?
The portal manages this process centrally with the GST portal, and the primary document to be submitted is RFD-01.
Step-by-Step Process:
1. Pre-application: Matching GSTR-3B and GSTR-1
2. Submit RFD‑01 online
3. Get ARN (Application Reference Number)
4.RFD‑02: Acknowledgment
5.RFD‑03: If deficiencies are found
6.RFD‑06: Final refund sanction order
Documents for GST refund
- Form GST RFD-01 application
- Prescribed statements based on refund type
- Invoices, BRC/FIRC (for export of services), shipping bill/bill of export (for goods)
- Declaration under second & third proviso to Section 54(3)
- Undertaking/declaration under Sections 16(2)(c) & 42(2)
RFD-01 required documents:
Invoices and debit/credit notes related to the refund claim
- Shipping bills, BRC/FIRC for export refunds
- SEZ endorsement with declaration (no tax collected)
- Invoice statement for inverted duty claims
- Self-declaration for refund < ₹2 lakh
- CA/Cost Accountant certificate for refund > ₹2 lakh
GST refund deficiency memo:
A GST officer issues a GST Refund Deficiency Memo (Form RFD-03) in case all conditions of a given refund application, as submitted in Form RFD-01, are deficient or incorrect. If a refund claim in Form RFD-01 is found deficient, the GST officer issues Form RFD-03 within 15 days under Rule 90(3). This memo takes the initial application as invalid and mandates that the taxpayer correct the mistakes and make another RFD-01 with a different ARN, which has to be within 2 years as initially set.
Reply to the GST refund notice
In case your refund request is incomplete:
- Respond in detail and submit Form RFD-09, then file a new RFD-01 after correcting mistakes.
- A timely response helps avoid delays or rejection.
Provisional GST refund
In the circumstances where there is a claim to refund of taxes paid on export of goods or services, other than the refund of accumulated Input Tax Credit (ITC), up to a total provision of the refund claim, 90 per cent shall be provisionally sanctioned to the applicant within 7 days of the acknowledgment of the claim. This provision guarantees liquidity on a timely basis among the exporters with checks of compliance in the form of final scrutiny.
GST refund RFD-06 :
For GST refund RFD-06, the following points are to be considered:
i) Sum on refund/interest: Actual amount claimed by the applicant.
ii) Refund Sanctioned on Provisional Basis (Order No date): Enter details of any amount already refunded provisionally.
iii) Amount inadmissible to refund: Mention the amount not eligible for refund with reasons (multiple reasons allowed).
iv) Gross to pay (1-2-3): Difference of amounts in points (i), (ii), and (iii).
v) Refund adjusted against outstanding demand: If any demand exists, it’s adjusted against the refund (mention Demand Order No., date, Act, and period).
vi) Net Amount to be paid: Final sanctioned refund amount as per the order
GST Refund Of Form RFD-02
There is an acknowledgment that comes under the scheme RFD-02, which is there on the common portal to the applicants. The application of self-assessment of the refund can be applied on the form GST RFD-01 of the common portal, whose acknowledgment will be auto-populated on the common portal.
The acknowledgment is auto-populated and includes:
- Acknowledgment number
- Date of issue
- GSTIN/UIN/Temporary ID
- Name of applicant
- Jurisdiction (Centre/State/UT)
- Form number
- Name of authorized signatory
- Tax period of the refund application
- Date and time of refund filing
- Reason for refund claim
Special Cases & Use Cases
Some GST refund scenarios require additional understanding:
- Inverted Duty Structure – Refund calculated per Rule 89(5). No refund on input services.
- Export Without Payment – Allowed under Letter of Undertaking (LUT). Apply for ITC refund.
- SEZ Supplies – Treated as zero-rated, must submit SEZ endorsement and supplier invoice.
GST refund export without payment
Exporters who supply goods or services without payment of IGST under LUT are eligible to claim a refund of unutilized ITC. After filing GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B, the refund must be claimed through Form RFD-01. Ensure that invoices, shipping bills, EGM, and BRC/FIRC (for services) are correctly matched to avoid delays.
Help Resources & MyGSTRefund
Exporters often face GST refund delays due to portal issues, document errors, or a lack of expert guidance. MyGSTRefund solves this with automated matching of invoices, shipping bills, and bank details, real-time ARN tracking, Refund calculator , ready RFD-09 responses, and tailored support for LUT, SEZ, and inverted duty refunds, ensuring faster, error-free claims.
GST Refund Helpline (MyGSTRefund): +91 92891 92891
Check: www.mygstrefund.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the time limit for taking a refund?
The time limit for the individual claiming a refund is required to apply before the expiry of two years from the “relevant date” as given in the Explanation to section 54 of the CGST/TSGST Act.
2. Can I track the status of the Refund Pre-Application Form after its submission?
Unfortunately , there is no tracking functionality available after the Refund Pre-Application Form is submitted on the GST Portal.
3. Is it possible to trace a refund by ARN?
Yes, it can be checked using the status checker of the GST portal or MyGSTRefund
dashboard.
4. What if my refund is under ₹1,000?
No refund shall be granted if the amount is less than Rs 1000/-. [Sec. 54 (14) of the CGST/TSGST Act].
Related Posts








