Comprehensive Guide to Shipping Bill Types & Formats
A Shipping Bill is a crucial document according to Indian Customs Laws, which acts as a clearance of goods exported out of India. It is a mandatory requirement to export goods, and it's one of the major documents in customs clearance. The information provided in shipping bills is regarding the goods, the exporter, the consignee, and the export schemes applicable to it.
Additionally, it serves as a prerequisite for receiving export-related incentives, such as Export GST Refund, Duty Drawback, or other state initiatives.
Purpose and Importance of the Shipping Bill:
Customs Clearance
The Shipping Bill is the primary document used for customs clearance during export. Customs authorities use it to assess classification, valuation, and determine the eligibility for duty exemptions or export incentives.
Export Declaration
The Shipping Bill forms a declaration to the effect that the exporter is exporting goods, and the goods comply with the existing laws and regulations of the country to be used in international trading.
Legal Requirement
According to Section 50 of the Customs Act, 1962, an export requires the Shipping Bill to be filed. It doesn't permit the products to exit the indian territory in its absence
Trigger for Export Process
Once filed, the Shipping Bill initiates the export chain, including documentation like the Bill of Lading or Airway Bill, and helps monitor the Shipping Bill status throughout the process.
Major Components of the Shipping Bill
Exporter’s Information:
This includes the exporter’s name, address, and registration details. It also has the IEC Code (Import Export Code) and contact information like phone number or email.
Consignee’s Information:
This section contains the name and address of the buyer (person or company receiving the goods) and the country where the goods are being sent.
Details of Goods:
- Description: What kind of goods are being exported?
- HSN Code: A code that is used to classify goods for customs.
- Quantity and Value: The amount and quantity of how much of goods being exported and their total value.
- Packaging Details: The details of how the goods are packed, the number of boxes, total weight, etc.
- Customs Tariff: The classification of tac category to which the goods fall.
- Country of Origin: The country into which the goods have been processed or manufactured.
Export Declaration:
The exporter confirms that the goods follow all export rules and that duties (if any) are paid correctly. It also includes a note if the exporter is claiming Duty Drawback or other government export benefits.
It consists of an Export Declaration where the Compliance statement and incentive claim statement (e.g., under Duty Drawback or RODTEP), along with the port of export, referring to the specific Indian port (Mumbai, Chennai, or Kolkata) from which goods will be shipped internationally and the transport medium which indicates whether the goods will be moved by sea, air, or road.
Customs Duty and Incentive Details:
Shows if any customs duty needs to be paid or if there are any exemptions. It also mentions if the exporter is eligible for schemes like Duty Drawback or EPCG (Export Promotion Capital Goods).
Shipping Details:
Information about the shipping company and vessel name for sea exports, Airway Bill number for air shipments, and container details if goods are sent in containers.
Exporter’s Declaration:
A final confirmation from the exporter saying that all the details given are true and follow Indian Customs rules.
Types of Shipping Bills under Indian Customs Laws
Depending on the nature of the export transaction and the export scheme under which goods are being exported, several types of Shipping Bills are issued:
Drawback Shipping Bill: Filed to claim a refund of duties paid on imported inputs used in goods meant for export.
Export Promotion Shipping Bill: For exports under schemes like Advance Authorization or EPCG.
Free Shipping Bill: Used when no incentives or duty drawbacks are claimed.
Gift Shipping Bill: For low-value gifts exported without claiming any customs benefits.
Postal Shipping Bill: For small consignments via post or courier.
Duty-Free Shipping Bill: Applicable when goods are exported under FTA agreements or re-exported without duty.
Understanding the Shipping Bill Format
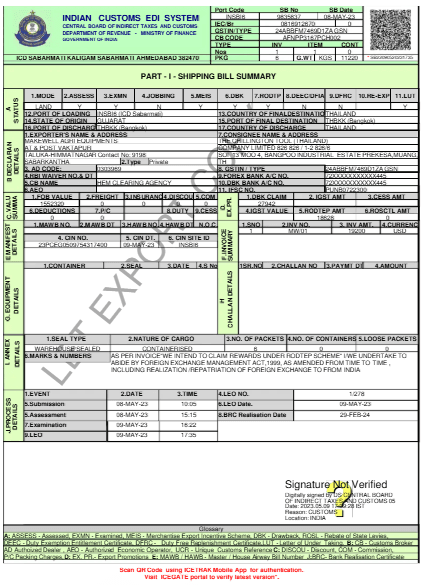
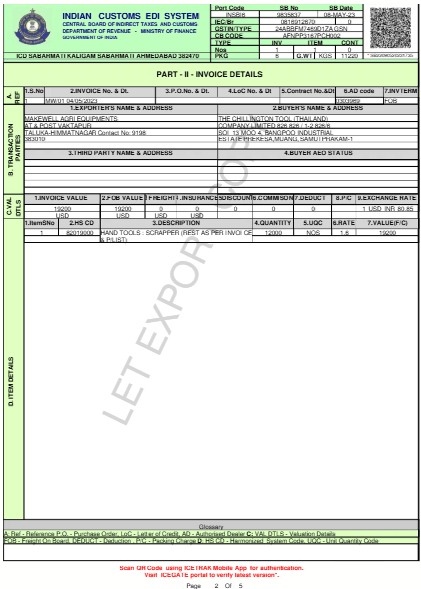
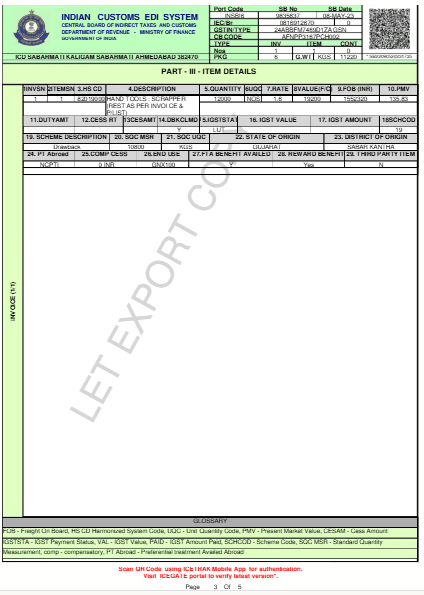
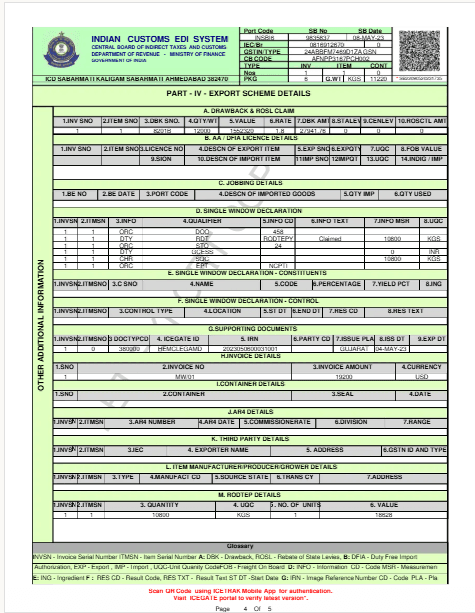
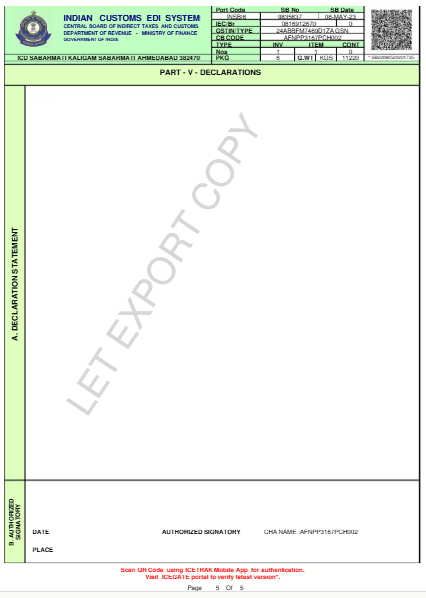
Procedure for Filing the Shipping Bill
Pre-Export Preparations
Clearance of exporters to have a valid IEC Code issued by the DGFT and classification of goods according to the correct HSN code
Filing the Bill
Exporters must file the Shipping Bill electronically through the ICEGATE portal. In rare exceptions, manual filing at Customs Ports is allowed.
Customs Processing
After submission of the shipping bill, Customs verifies the documents like invoices, packing lists, and product classification. Physical examination may be carried out based on risk assessment.
Let Export Order (LEO)
The Clearing of the stage of export duty (where applicable) and verification stages (where applicable) results in the approval of the Let Export Order (LEO) being issued by Customs.
Post-Export and Shipment Compliance
Goods are then loaded and exported. The exporter must retain the Shipping Bill copy as proof to claim export benefits like Export GST Refund, Duty Drawback, or Export Finance assistance.
Customs Procedures and Compliance
Verification and regulation
The way customs may examine their goods to be sure that they contain what is declared is either by physical examination or by checking documents. This makes sure that goods meet the export laws, such as strategic or limited items.
Export Control Compliance
The exporters are required to comply with the export control legislation in India, the trade restrictions and prohibitions in the existing foreign trade policy.
Bonuses and Rebates
The Shipping Bill plays an essential role in taking government opportunities. This document will be your foundation in your refund application, whether you are applying for RODTEP, ROSCTL, or Export GST Refund.
During your export finance activities, nowadays, proper documentation of your Shipping Bill status can aid in increased transparency in the deal at the financing level of partners once you address your Export Finance needs.
Conclusion
The Shipping Bill is a fundamental document in the Indian Customs export procedure. It is a statement of the nature of the goods being exported to the Customs officers and crucial to the payment of the applicable customs duty, the observance of the rules of trade, the claim of privileges, or even discounts such as drawback of duties or exemptions.
The Shipping Bill must be properly filed and within the required time frames to ease the exportation of goods. Exporters should also take care that they satisfy all the compliance conditions associated with the exportation of goods by ensuring that documentation, classification, and valuation are properly observed in order to prevent delays and monetary penalties.
Read More: Export Finance
Related Posts







